Comparing NMEA 2000 Backbone and Drop Cable
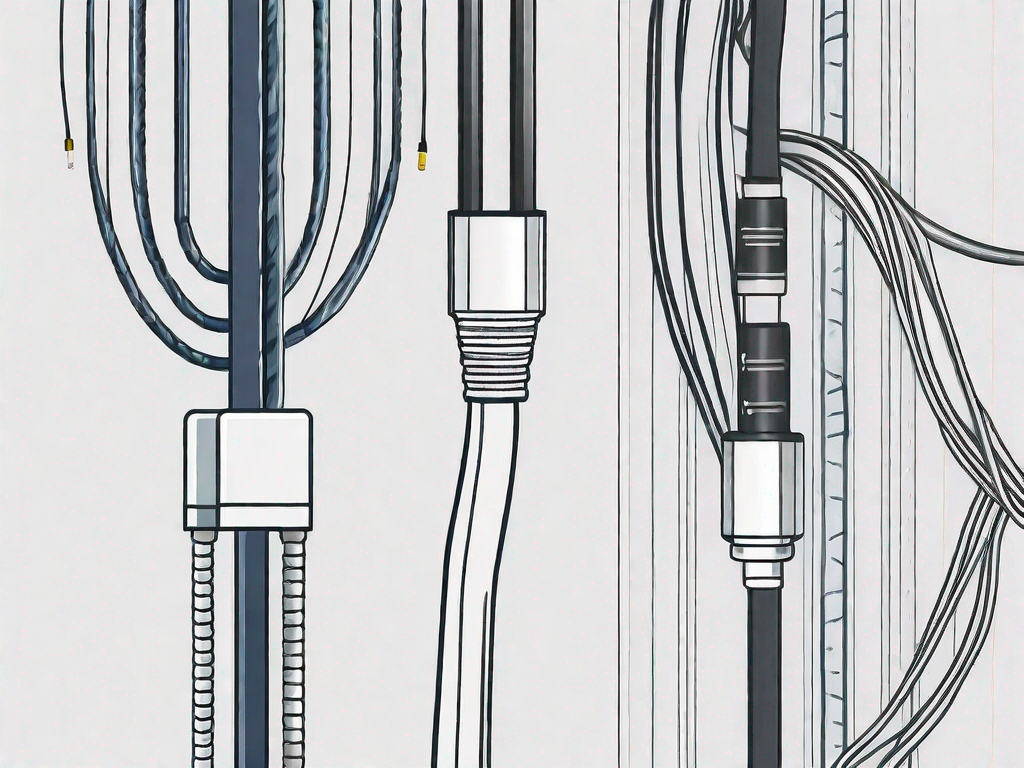
The NMEA 2000 network has revolutionized the world of marine electronics, providing a robust and efficient way to connect various devices and instruments on board a vessel. One of the key components of this network is the backbone cable, which forms the main communication pathway, and the drop cable, which connects individual devices to the backbone. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is crucial for building and maintaining a reliable NMEA 2000 network.
Understanding NMEA 2000 Network
Before we delve into the specifics of backbone and drop cables, let's take a moment to grasp the basics of the NMEA 2000 network. This standardized network allows different marine electronics devices to communicate seamlessly, enabling data sharing and integration. Whether it's a GPS unit, depth sounder, or a chartplotter, all these devices can work together and provide valuable information to the boater.
Central to the NMEA 2000 network is the backbone cable, which serves as the main communication highway. It connects various devices and instruments, allowing them to exchange data effortlessly. Connected to the backbone are the drop cables, which provide the individual connections between devices and the backbone. These drop cables ensure that each device has a dedicated link to the backbone.
Basics of NMEA 2000 Network
The NMEA 2000 network operates on a plug-and-play principle, making it easy to expand and modify as per the boater's needs. Devices can simply be connected to the network by plugging them into the backbone using drop cables. This simplicity and scalability have made the NMEA 2000 network the go-to choice for marine electronics integration.
Furthermore, the NMEA 2000 network utilizes a robust communication protocol, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission. This protocol allows multiple devices to communicate simultaneously, utilizing a high-speed data bus. Thanks to this advanced protocol, the NMEA 2000 network can handle a vast amount of data, making it suitable for even the most demanding marine applications.
Importance of NMEA 2000 Network in Marine Electronics
Having a well-designed NMEA 2000 network is essential for maximizing the functionality and performance of marine electronics. By seamlessly integrating different devices, boaters can take advantage of features like sharing data across devices, displaying information on multiple screens, and controlling various devices from a single interface.
Furthermore, the NMEA 2000 network simplifies installation and reduces the amount of cabling required. Instead of running separate cables for each device, a single backbone cable can be used, greatly simplifying the installation process. This not only saves time and effort but also eliminates clutter and ensures a cleaner and more organized installation.
One of the key advantages of the NMEA 2000 network is its ability to provide real-time data updates. This means that boaters can receive accurate and up-to-date information about their vessel's position, speed, depth, and other important parameters. This real-time data is crucial for navigation, allowing boaters to make informed decisions and ensure the safety of their vessel and crew.
In addition to real-time data updates, the NMEA 2000 network also enables boaters to access historical data. This means that they can review past trips, analyze performance, and identify trends or patterns. By having access to this historical data, boaters can make informed decisions about their vessel's maintenance, fuel consumption, and overall performance.
Another advantage of the NMEA 2000 network is its ability to support third-party devices and applications. This means that boaters can choose from a wide range of compatible devices and software, allowing them to customize their marine electronics system according to their specific needs and preferences. Whether it's integrating a fishfinder, weather station, or autopilot system, the NMEA 2000 network provides the flexibility to expand and enhance the functionality of the marine electronics setup.
Furthermore, the NMEA 2000 network promotes energy efficiency and reduces power consumption. By utilizing a single backbone cable and efficient data transmission protocols, the network minimizes the overall power requirements of the marine electronics system. This is particularly important for boaters who rely on battery power, as it helps prolong battery life and ensures uninterrupted operation of essential devices.
In conclusion, the NMEA 2000 network is a powerful and versatile solution for integrating marine electronics devices. Its plug-and-play nature, robust communication protocol, and scalability make it an ideal choice for boaters looking to maximize the functionality and performance of their marine electronics system. Whether it's enhancing navigation capabilities, accessing real-time and historical data, or customizing the system with third-party devices, the NMEA 2000 network offers endless possibilities for seamless integration and data sharing.
Deep Dive into NMEA 2000 Backbone Cable
Now that we have a good understanding of the NMEA 2000 network, let's take a closer look at the backbone cable. This cable plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and reliable communication between devices on the network.
The backbone cable serves as the main pathway for data transmission in the NMEA 2000 network. It connects all the devices together, forming a comprehensive network. Without a properly functioning backbone cable, the network would be fragmented, and the devices wouldn't be able to communicate effectively.
Designed to withstand the harsh marine environment, backbone cables are typically constructed with high-quality materials to ensure longevity and durability. They feature robust connectors that provide secure and reliable connections, even in rough seas or unfavorable conditions.
But what exactly makes the backbone cable so reliable? One key feature is its ability to resist water and corrosion. This is achieved through the use of specialized materials and coatings that protect the cable from moisture and other environmental factors. Whether it's saltwater or heavy rain, the backbone cable is designed to keep the network running smoothly.
Another important aspect of the backbone cable is its flexibility. These cables come in various lengths, allowing for flexibility in network design and installation. Whether you have a small vessel or a large yacht, you can customize the length of the backbone cable to match the specific requirements of your vessel. This ensures efficient communication between devices at different locations.
Furthermore, the connectors used in backbone cables are designed to be watertight and corrosion-resistant. This is crucial in marine applications where exposure to water and salt can cause damage to the connectors over time. The robust connectors ensure that the network remains reliable, even in challenging conditions.
When it comes to installation, the backbone cable is typically routed through strategic areas of the vessel. This ensures that it is protected from potential damage and interference. Proper cable management techniques are employed to secure the cable and prevent any accidental disconnections.
Overall, the backbone cable is an essential component of the NMEA 2000 network. It provides the necessary infrastructure for devices to communicate seamlessly and ensures reliable data transmission. With its durability, flexibility, and resistance to water and corrosion, the backbone cable is designed to withstand the demanding conditions of the marine environment.
Functionality of Backbone Cable
The backbone cable serves as the main pathway for data transmission in the NMEA 2000 network. It connects all the devices together, forming a comprehensive network. Without a properly functioning backbone cable, the network would be fragmented, and the devices wouldn't be able to communicate effectively.
Designed to withstand the harsh marine environment, backbone cables are typically constructed with high-quality materials to ensure longevity and durability. They feature robust connectors that provide secure and reliable connections, even in rough seas or unfavorable conditions.
Key Features of Backbone Cable
Backbone cables come in various lengths, allowing flexibility in network design and installation. They can be customized to match the specific requirements of a vessel, ensuring efficient communication between devices at different locations.
Moreover, backbone cables often have waterproof and corrosion-resistant properties, making them suitable for marine applications. This ensures that the network remains robust and reliable, even in challenging conditions.
Exploring NMEA 2000 Drop Cable
While the backbone cable forms the main communication pathway, the drop cable connects individual devices to the network. These cables allow each device to receive and transmit data to other devices on the NMEA 2000 network.
Role of Drop Cable in NMEA 2000 Network
Drop cables serve as the links between the individual devices and the backbone cable. They allow each device to have its dedicated connection to the network, ensuring efficient data transfer and reliable communication.
Just like the backbone cable, drop cables are designed to withstand the rigors of the marine environment. They are made with high-quality materials that provide excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion, ensuring a long-lasting and reliable connection for years to come.
Characteristics of Drop Cable
Drop cables come in different lengths to accommodate various installation scenarios. Whether you need a short cable to connect a device in close proximity to the backbone or a longer cable to reach a device located further away, there are options available to fit your needs.
Furthermore, drop cables are often equipped with waterproof connectors, ensuring that they maintain a secure and reliable connection even when exposed to moisture. This feature is especially important in marine environments, where moisture and saltwater can be common.
Differences Between Backbone and Drop Cable
While both backbone and drop cables are integral parts of the NMEA 2000 network, there are some notable differences between the two. These differences, both technical and functional, determine the specific roles and characteristics of each cable.
Technical Differences
From a technical standpoint, the main difference between the backbone and drop cables lies in their construction and purpose. The backbone cable serves as the main communication pathway, connecting all the devices on the network. On the other hand, the drop cable provides the individual connections between devices and the backbone, facilitating data exchange between specific devices.
Functional Differences
Functionally, the backbone cable ensures that all devices on the network can communicate seamlessly, whereas the drop cable allows individual devices to transmit and receive data. The backbone cable creates a comprehensive network, while the drop cable enables precise device-to-device communication.
Another significant functional difference is the length and flexibility of the cables. Backbone cables are typically longer and more customizable, as they need to span larger distances and accommodate various devices. Drop cables, on the other hand, are often shorter and more tailored to specific device connections.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
When it comes to building or expanding your NMEA 2000 network, selecting the right cable is crucial. Consider the following factors to ensure you make the best choice for your specific needs.
Factors to Consider
First and foremost, consider the length requirements of your network. Measure the distances between devices and determine the necessary length of the backbone and drop cables accordingly. Additionally, pay attention to environmental factors such as exposure to water, UV rays, and extreme temperatures. Choose cables with appropriate protection to ensure longevity and reliable performance.
Furthermore, take into account the number of devices you plan to connect to the network. Ensure that the backbone and drop cables can handle the required bandwidth and data transfer rates. It's also worth considering future expansion and scalability, as you might want to add more devices to your network down the line.
Tips for Making the Right Choice
Seek advice from reputable marine electronics professionals or consult manufacturer documentation for guidance on selecting the right cables. They can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed decision.
Lastly, consider purchasing cables from trusted brands that have a proven track record in the marine industry. Quality cables not only ensure reliable data transmission but also provide excellent durability and resistance to harsh marine conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between NMEA 2000 backbone and drop cables is essential for building a reliable and efficient marine electronics network. The backbone cable forms the main communication pathway, while the drop cables facilitate individual device connections to the network. By selecting the right cables and adhering to best practices, you can ensure seamless data exchange and enhanced functionality of your marine electronics system.













![Siren Marine Battery Sensor f/Siren 3 [SM-WLS3-BATT-917] - Themarineking.com](http://themarineking.com/cdn/shop/products/85429XL_{width}x.jpg?v=1648740446)

![Minn Kota Raptor Jack Plate Adapter - Starboard - 2" Setback - 6" Rise - Black [1810362] - Themarineking](http://themarineking.com/cdn/shop/products/85198XL_{width}x.jpg?v=1648572090)





















